Geological maps
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
-
Manuscript geological maps produced by the Survey geologists or other recognised geologists on County Series (1:10560) and National Grid (1:10560 & 1:10000) Ordnance Survey base maps of Great Britain. A small number are produced at larger scale. Similar maps compiled from other sources. Maps produced since the 1850's, current holdings over 35,000 maps, all now scanned and available internally as image files.
-
This dataset comprises scanned images of the manuscript geological maps produced by the Survey geologists or other recognised geologists on County Series (1:10560) and National Grid (1:10560 and 1:10000) Ordnance Survey base maps. The collection also includes similar maps compiled from other sources. Currently the dataset contains over 35,000 scanned images. Original maps date from the 1860s, and cover surveys in Great Britain, scanning started in 2003.
-
Index to BGS geological map 'Standards', manuscript and published maps for Great Britain produced by the Survey on County Series (1:10560) and National Grid (1:10560 & 1:10000) Ordnance Survey base maps. 'Standards' are the best interpretation of the geology at the time they were produced. The Oracle index was set up in 1988, current holdings are over 41,000 maps. There are entries for all registered maps, but not all fields are complete on all entries.
-
Geological map 'Standards', manuscript and published maps of Great Britain produced by the Survey on County Series (1:10560) and National Grid (1:10560 & 1:10000) Ordnance Survey base maps. Maps produced since the 1860's, current holdings over 41,000 maps, all now available internally as image files.
-
Index to manuscript geological maps produced by the Survey geologists or other recognised geologists on County Series (1:10560) and National Grid (1:10560 & 1:10000) Ordnance Survey base maps. The index was set up in 1991. Current holdings for Great Britain are over 35,000. There are entries for all registered maps but the level of detail depends on nature of original Survey, ie not all fields are complete for all entries.
-
Photographic negatives of Geological map 'Standards', manuscript and published maps produced by the Survey on County Series (1:10560) and National Grid (1:10560 & 1:10000) Ordnance Survey base maps. Current holdings over 41,000 maps for Great Britain. The majority of maps were scanned in 2004, any new maps produced are scanned and added to the collection. This is essentially a back up collection for disaster recovery.
-
The index shows the availability of county series geological maps, 1:10560 scale. The maps themselves were produced on OS County Series sheets between approximately 1860 and 1960. The list indicates whether the map has been revised or re-surveyed and gives details of any later versions that have been produced. It is advisable to discuss your requirements before ordering or travelling to view these maps.
-
Data identifying landscape areas (shown as polygons) attributed with geological names. The scale of the data is 1:10 000 scale. Onshore coverage is partial with approximately 30% of England, Scotland and Wales available in this version 2 data release. BGS intend to continue developing coverage at this scale; current focus is to include all large priority urban areas, along with road and rail transport corridors. Data are supplied as five themes: bedrock, superficial deposits, mass movement, artificial ground and linear features. Bedrock geology describes the main mass of solid rocks forming the earth's crust. Bedrock is present everywhere, whether exposed at surface in outcrops or concealed beneath superficial deposits or water bodies. Geological names are based on the lithostratigraphic or lithodemic hierarchy. The lithostratigraphic scheme arranges rock bodies into units based on rock-type and geological time of formation. Where rock-types do not fit into the lithostratigraphic scheme, for example intrusive, deformed rocks subjected to heat and pressure resulting in new or changed rock types; then their classification is based on their rock type or lithological composition. This assesses visible features such as texture, structure, mineralogy. Superficial deposits are younger geological deposits formed during the most recent geological time; the Quaternary. These deposits rest on older rocks or deposits referred to as bedrock. The superficial deposits theme defines landscape areas (shown as polygons) attributed with a geological name and their deposit type or lithological composition. Mass movement describes areas where deposits have moved down slope under gravity to form landslips. These landslips can affect bedrock, superficial or artificial ground. Mass movement deposits are described in the BGS Rock Classification Scheme Volume 4. However the data also includes foundered strata, where ground has collapsed due to subsidence (this is not described in the Rock Classification Scheme). Caution should be exercised with this data; whilst mass movement events are recorded in this layer, due to the dynamic nature of occurrence significant changes may have occurred since the data was released, as such it should be viewed as a snapshot in time (data should be regarded as at 2008). Artificial (man-made) theme (shown as polygons) indicates areas where the ground surface has been significantly modified by human activity. Whilst artificial ground may not be considered as part of the 'real geology' of bedrock and superficial deposits it does affect them. Artificial ground impacts on the near surface ground conditions which are important to human activities and economic development. Due to the constantly changing nature of land use and re-use/redevelopment, caution must be exercised when using this data as it represents a snapshot in time rather than an evolving picture hence the data may become dated very rapidly. Linear features (shown as polylines) represent geological structural features e.g. faults, folds or landforms e.g. buried channels, glacial drainage channels at the ground or bedrock surface (beneath superficial deposits). Linear features are associated most closely with the bedrock theme either as an intrinsic part of it for example marine bands or affecting it in the case of faults. However landform elements are associated with both bedrock and superficial deposits. All five data themes are available in vector format (containing the geometry of each feature linked to a database record describing their attributes) as ESRI shapefiles and are available under BGS data licence.
-
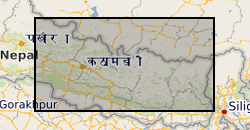
Raster (TIFF) file showing the simplified main bedrock geology units that comprise a ~45,000 km2 region of central-eastern Nepal.
-
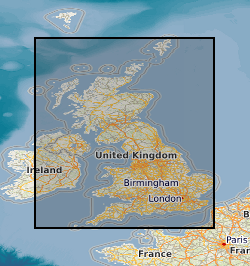
Data identifying landscape areas (shown as polygons) attributed with geological names. The scale of the data is 1:25 000 scale. Onshore coverage is partial and BGS has no intention to create a national coverage at this scale. Areas covered are essentially special areas of 'classic' geology and include Llandovery (central Wales), Coniston (Lake District) and Cuillan Hills (Isle of Skye). Data are supplied as five themes: bedrock, superficial deposits, mass movement, artificial ground and linear features. Bedrock geology describes the main mass of solid rocks forming the earth's crust. Bedrock is present everywhere, whether exposed at surface in outcrops or concealed beneath superficial deposits or water bodies. The bedrock theme defines landscape areas (shown as polygons) attributed with geological names. Geological names are based on the lithostratigraphic or lithodemic hierarchy. The lithostratigraphic scheme arranges rock bodies into units based on rock-type and geological time of formation. Where rock-types do not fit into the lithostratigraphic scheme, for example intrusive, deformed rocks subjected to heat and pressure resulting in new or changed rock types; then their classification is based on their rock-type or lithological composition. This assesses visible features such as texture, structure, mineralogy. Superficial deposits are younger geological deposits formed during the most recent geological time; the Quaternary. These deposits rest on older rocks or deposits referred to as bedrock. The superficial deposits theme defines landscape areas (shown as polygons) attributed with a geological name and their deposit-type or lithological composition. Mass movement describes areas where deposits have moved down slope under gravity to form landslips. These landslips can affect bedrock, superficial or artificial ground. Mass movement deposits are described in the BGS Rock Classification Scheme Volume 4. However the data also includes foundered strata, where ground has collapsed due to subsidence (this is not described in the Rock Classification Scheme). Caution should be exercised with this data; whilst mass movement events are recorded in this layer, due to the dynamic nature of occurrence significant changes may have occurred since the data was released, as such it should be viewed as a snapshot in time (data should be regarded as at 2008). Artificial (man-made) theme (shown as polygons) indicates areas where the ground surface has been significantly modified by human activity. Whilst artificial ground may not be considered as part of the 'real geology' of bedrock and superficial deposits it does affect them. Artificial ground impacts on the near surface ground conditions which are important to human activities and economic development. Due to the constantly changing nature of land use and re-use/redevelopment, caution must be exercised when using this data as it represents a snapshot in time rather than an evolving picture hence the data may become dated very rapidly. Linear features (shown as polylines) represent geological structural features e.g. faults, folds or landforms e.g. buried channels, glacial drainage channels at the ground or bedrock surface (beneath superficial deposits). Linear features are associated most closely with the bedrock theme either as an intrinsic part of it for example marine bands or affecting it in the case of faults. However landform elements are associated with both bedrock and superficial deposits. All five data themes are available in vector format (containing the geometry of each feature linked to a database record describing their attributes) as ESRI shapefiles and are available under BGS data licence. Another batch of tiles was added to the data in 2012 to bring the total to 167 for this version 2 release.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service